Is Web3 the Next Big Thing? A CIO and CEO Perspective
Web 3.0, popularly known as Web3, is the new buzzword in the technology space. It has evolutionary similarities with Industry 4.0 which has evolved from its version 1.0 over decades. While Industry 4.0 is also about emerging technologies but is related mostly to industrial applications, Web 3.0 refers to the technology application on the internet and the web. Most online and virtual activities will be in Web3 space in the days to come.
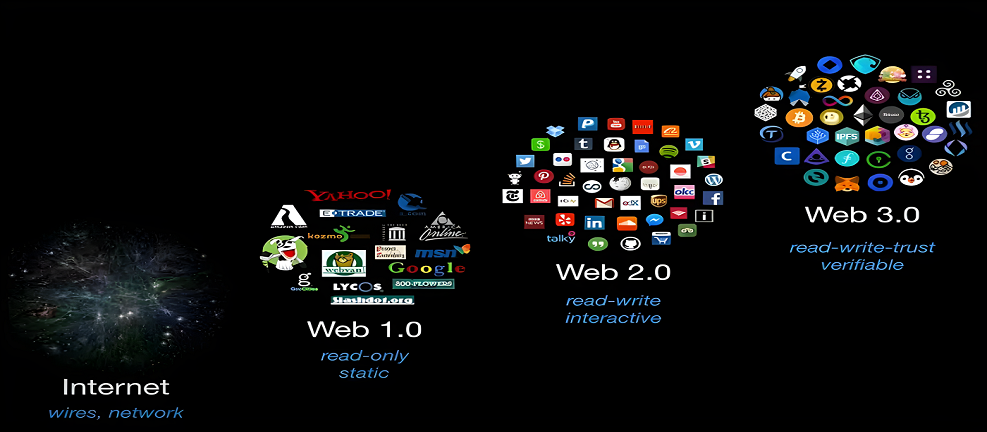
Web 1.0 is the first version of the internet and web that emerged in the early 1990s. Web1 pages were static where the users could only view content and not interact. Those were the days of internet heroes like Britannica Online or Yahoo which were supported by protocols like IP, HTTP, and coding languages like HTML, among others.
The debacle of the dot-com in 2000 did not stop some top brains in the tech world from innovating and developing technologies such as JavaScript, HTML5, and CSS3 that facilitated the gradual growth of Web2 (Web 2.0). This has made interaction possible on the internet allowing users to interact and provide data to social media, e-commerce portals, or payment providers, facilitating the functioning of these apps. Social media platforms like Facebook, and Twitter, messaging apps like WhatsApp, and payment service providers like PhonePay, and GooglePay are examples of Web2. We are currently in the Web2 stage transitioning to Web3.
Web2 has significantly changed the way we communicate and interact, consume content, make phone calls via messaging apps like WhatsApp and Telegram, shop online on e-commerce platforms like Amazon, watch movies and shows on OTT platforms like Netflix, stay in the house of other people by booking through Airbnb, and make online payment using fintech platforms. While these have been revolutionary changes in how we live life, run businesses, and conduct governance, there arose a lot of criticism and litigation alleging violation and compromise of privacy of the user data which is stored and controlled by central servers of content providers.
Most Web2 applications are under the control of corporations or entities, including banking and financial services, resulting in creating barriers to entry and restricting fair play. This is where Web3 has emerged to disrupt the power center of the market players by replacing the centralized server with decentralized systems, such as blockchain. This ensures that all data will be distributed across a decentralized network, making centralized entities irrelevant.
Here is an example: Imagine a person sending money to another person today, it involves a bank as an intermediary and central server that maintains all required data for facilitating the transaction. The user must provide all relevant data to the banks for them to execute the transaction for a fee for this service. This is banking in Web2. Web3 allows you to send money via a decentralized blockchain, which independently verifies the transaction for its correctness and authenticity by employing a consensus algorithm. There is no intermediary like a bank involved here, which allows the users to make the transactions free of cost without compromising on control and privacy over the transactions.
While it is believed that the Netscape web browser initiated Web1, the foundation of Web3 was the emergence of blockchain technology and the launch of the Bitcoin cryptocurrency built on blockchain. The cryptocurrency that uses a decentralized or distributed network works on a peer-to-peer (P2P) concept without the need for banks or central banks to monitor, control, or manage transactions and records.
Ethereum blockchain which came after Bitcoin and is the second largest and most popular blockchain network has developed many innovative solutions to take blockchain beyond cryptocurrency including decentralized finance and smart contracts that replace intermediaries, such as banks, monetary authorities, and governments, through trustless networks.
Non-fungible tokens ("NFTs"), another Web3 application, represent a unique digital form of ownership of real-world assets, such as graphics, artwork, tweets, painting, music, real estate, or domain. As NFTs, one-of-its-kind unique digital assets, are non-fungible; they cannot be exchangeable with the same type of tokens and enable evidence of authentic ownership and their digital transfer without centralized intermediaries. NFT is the opposite of Crypto in the sense that crypts are fungible whereas NFTs are not.
The foremost challenge of Web3 at present is the processing speed which is significantly lower compared to applications in the centralized Web2. Performing a bitcoin transaction, for example, takes much more time and energy than a Web2 transaction done through fintech platforms takes. Furthermore, Web3 is still more complicated for many users to use than Web2 applications.
More importantly, Web3 is still not fully decentralized in real terms as most applications under Web3 still need Web2 infrastructure. For example, if the cloud services such as Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure break down, most Web3 applications would also be down.
Legal and regulatory aspects is another challenge that needs to be addressed. Cryptocurrency and dependent applications like DeFi are not legally recognized in most countries and are banned in some countries. While blockchain technology can be adopted for other use cases, the financial application will remain a significant challenge till the time a regulatory framework that can be applied across countries globally evolves.
There is no debate on whether Web3 will evolve or not. It has taken three decades for Web2 to evolve and mature. The token economy, that is Web3, is the next big thing in technology though we are not sure yet how this evolution will take shape. Decentralized networks and protocols will collaborate and compete with centralized platforms for some time till platforms that are independent of centralized platforms evolves.
In addition to financial applications, Web 3.0 could find applications in various areas like changing the traditional organizational structure to autonomous organizations or in democratic elections of representatives for countries. The power of Web3 lies in its capability to democratize processes replacing the current centralized or controlled setups. All these use cases could eventually culminate in the so-called metaverse: The metaverse is a virtual reality world where people communicate, do business, trade, play, learn, or otherwise interact with each other.
Once Web3 matures and innovates further, we will be living in a new world where those not embracing Web3 may be left behind in the race. While large enterprises may have internal resources to pursue adopting Web3, small businesses including startups will find it challenging unless they leverage platforms like AiDOOS Task as a Service (TaaS) to build their Web3 applications.
As organizations explore the decentralized future promised by Web3, Virtual Delivery Centers (VDCs) play a critical role in enabling seamless transitions and unlocking the full potential of the next generation of the internet. Here’s how VDCs align with Web3 innovations:
Access to Blockchain Experts: VDCs provide a curated pool of blockchain developers and smart contract specialists to build secure, scalable, and efficient decentralized applications (dApps).
Integration of Web3 Technologies: Transitioning to Web3 involves integrating blockchain, decentralized storage, and tokenized economies. VDCs streamline this integration process, ensuring compatibility and functionality.
Smart Contract Development: VDCs specialize in creating and deploying smart contracts that form the backbone of decentralized applications, ensuring reliability and transparency.
Scalability and Cost Efficiency: Through the VDC model, businesses can scale their Web3 projects on demand, optimizing resource allocation while minimizing costs.
Governance and DAOs: Web3 introduces decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). VDCs assist businesses in designing and managing governance models for DAOs to enhance decentralized decision-making.
Token Economy Design: Web3 projects often involve tokenization. VDCs provide expertise in designing token economics that incentivize participation and foster ecosystem growth.
Cybersecurity and Privacy: With decentralized systems come new security challenges. VDCs implement robust measures to safeguard data, ensure private transactions, and protect decentralized networks.
Rapid Prototyping and Testing: Web3 is still an evolving ecosystem. VDCs enable businesses to experiment with decentralized solutions, rapidly prototyping and testing ideas to ensure market readiness.
Education and Training: VDCs empower internal teams with Web3 knowledge, offering training programs that keep businesses aligned with the latest trends and innovations.
Global Collaboration: Web3 is inherently global, connecting users and businesses across borders. VDCs facilitate this collaboration by providing diverse talent and localized insights.
By leveraging VDCs, organizations can confidently embrace Web3, fostering innovation and creating decentralized solutions that redefine user experiences, improve transparency, and drive sustainable growth.

For modern telecom enterprises, delivering exceptional QoS is no longer optional—it’s a brand differentiator and a strategic lever for growth. Static provisioning models won’t cut it in a world of hyper-dynamic data usage.