How to Lead CRM Implementations for Success: A Guide for CIOs and IT Leaders

Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is more than just software; it’s a strategic approach that integrates technology, processes, and people to improve customer engagement, drive sales, and streamline operations. For CIOs and IT leaders in small to mid-sized businesses, successfully implementing a CRM system can be the cornerstone of digital transformation. However, CRM implementations often encounter pitfalls that prevent businesses from realizing their full potential.
This guide delves deep into the nuances of CRM implementation, offering actionable insights and a comprehensive framework to ensure success. From understanding the role of CRM systems to avoiding common mistakes, this guide equips IT leaders with the knowledge needed to lead impactful implementations.

CRM systems are software solutions that enable businesses to manage customer data, interactions, and relationships effectively. They encompass a wide range of applications, including:
Managing customer data and interactions.
Tracking leads and opportunities.
Automating marketing campaigns.
Enhancing customer support and service.
Streamlining contract and project management.
In essence, a CRM acts as the hub of customer-related activities, bridging gaps between sales, marketing, customer service, and operations. For IT leaders, it’s an opportunity to integrate tools that improve cross-departmental collaboration and create a seamless customer experience.
CRM systems are designed to:
Enhance Efficiency: By automating tasks and centralizing information, CRM systems eliminate redundant processes, allowing teams to focus on strategic goals.
Improve Customer Satisfaction: Quick access to customer data enables personalized interactions, fostering stronger relationships.
Drive Revenue Growth: CRM tools enable upselling and cross-selling opportunities by providing insights into customer preferences and purchasing behavior.
Enable Data-Driven Decisions: With real-time analytics and dashboards, businesses can monitor performance and adjust strategies dynamically.
To maximize ROI, an ideal CRM system should:
Reflect Your Sales Process: Align with the company’s unique workflows and sales strategies.
Deliver Value Across Teams: From sales and marketing to customer support, every team should benefit.
Be User-Friendly: Ensure the system is intuitive and easy to navigate.
Offer Anywhere Accessibility: Enable remote and on-the-go access through cloud or mobile platforms.
Integrate Seamlessly: Synchronize with existing tools such as email, social media, web forms, and ticketing systems.
Support Scalability: Grow with your business, accommodating new users and features without disruption.
Despite the benefits, many CRM projects fall short of expectations. Understanding the root causes of failure is crucial to avoiding them.
1. Lack of Clear Objectives
A successful CRM implementation starts with well-defined, measurable goals. Without clear objectives, the project lacks direction, making it difficult to evaluate success. Objectives should address:
Customer acquisition and retention goals.
Operational efficiencies.
User adoption metrics.
2. Poor CRM Strategy
A CRM strategy should align with business priorities and customer-centric outcomes. Without a roadmap that focuses on customer relationships, the implementation may devolve into a mere data management exercise, failing to deliver tangible business value.
3. Scope Creep
Uncontrolled changes in project scope—or “scope creep”—can derail timelines and budgets. Common areas of scope creep include:
Over-customization.
Inadequate planning for data migration.
Mismanagement of integration tasks.
4. Resistance to Change
CRM implementations often disrupt established workflows, leading to user resistance. Addressing this requires proactive change management strategies such as:
Conducting readiness assessments.
Offering comprehensive training programs.
Communicating the benefits clearly.
5. Poor Business Process Design
Outdated or inefficient business processes can hinder CRM success. IT leaders must collaborate with business stakeholders to:
Streamline workflows.
Automate repetitive tasks.
Continuously improve processes based on CRM data insights.
6. Lack of Integration
A CRM system that operates in isolation offers limited value. Integration with business strategies and other systems (ERP, marketing automation, etc.) ensures that customer data drives decision-making across the organization.
7. Overlooking Mobile and Cloud
In a mobile-first world, CRM systems must support mobile access. Similarly, cloud-based CRMs offer scalability and flexibility, reducing infrastructure costs and enabling faster deployments.
8. Treating CRM as an IT Project
While technology is a critical enabler, CRM implementations should prioritize user-centric design and business outcomes over technical specifications. Involve end-users early to ensure adoption and satisfaction.
1. Define Your Objectives
Identify specific, measurable goals that align with business priorities. Examples include improving lead conversion rates, reducing customer churn, or increasing cross-sell revenue.
2. Choose the Right CRM Platform
Evaluate platforms based on your business size, industry, and operational needs. Popular options include Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, and Microsoft Dynamics.
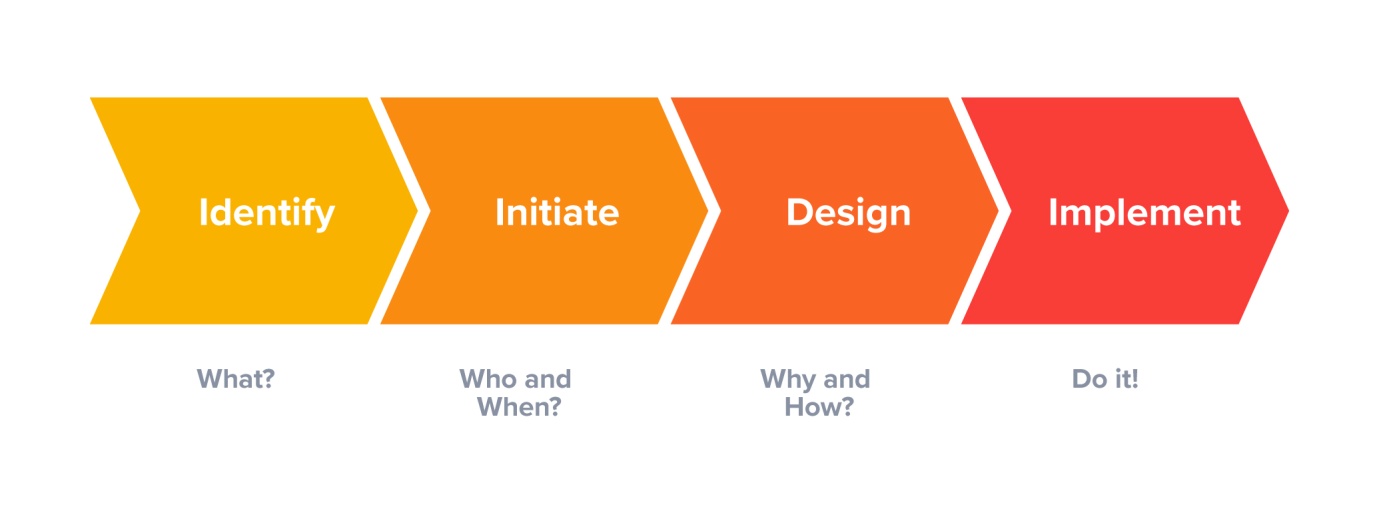
3. Create a Comprehensive Implementation Plan
Outline key phases, including:
Requirement gathering.
System design and configuration.
Data migration and integration.
User training and go-live support.
4. Involve Leadership and Build Credibility
Leadership buy-in is critical to project success. CIOs and IT leaders should champion the implementation, inspiring teams and securing resources.
5. Train and Motivate Users
Invest in user training to ensure team members can leverage the CRM effectively. Recognize and reward early adopters to drive engagement.
6. Continuously Monitor and Optimize
Use CRM analytics to monitor performance and refine processes. Regularly update the system to incorporate new features and address user feedback.
CRM implementations can be resource-intensive, requiring expertise in system configuration, data migration, and user training. Virtual Delivery Centers (VDCs) offer a scalable, cost-effective alternative to traditional in-house or outsourced teams.
Benefits of VDCs for CRM Implementations
Cost Efficiency: Reduce implementation costs by up to 70% by leveraging remote teams.
Access to Expertise: Tap into pre-vetted professionals with experience in CRM platforms and integration.
Scalability: Scale teams up or down based on project phases and requirements.
Faster Deployment: Benefit from 24/7 development cycles with distributed teams.
Continuous Support: Post-implementation support ensures your CRM system delivers sustained value.
By partnering with a VDC, IT leaders can overcome common challenges and achieve seamless CRM implementations, positioning their businesses for success in a competitive market.

For modern telecom enterprises, delivering exceptional QoS is no longer optional—it’s a brand differentiator and a strategic lever for growth. Static provisioning models won’t cut it in a world of hyper-dynamic data usage.